2sd test adverse impact large sample|adverse impact ratio calculation : suppliers The pooled two-sample z-score test is the statistical test recommended by the Office of . Summary. ‘Hyun-min’, a professor at a local university, is trou.
{plog:ftitle_list}
2 de set. de 2021 · Your browser is not able to display this video. O. Hanna Howo 0n|y F∆π$
The pooled two-sample z-score test is the statistical test recommended by the Office of .The chi-square test is a statistical test that is often used for analyzing adverse .Statistical tests evaluate the relationship between two or more variables that are .
a6300 weather sealing test
Adverse Impact Analysis. To calculate adverse impact, simply enter your .Adverse Impact Resources & Research. . (2005). Adverse Impact and Test .About Adverse Impact. Adverse impact is defined by the Uniform Guidelines as a .This paper reviews basic statistical significance tests for adverse impact (AI) analyses of 2x2 .
You can use the 4/5th rule, 2SD (standard deviation test) or chi-square test (fishers chi-square .
It is an estimator test based on large samples that approximates the precise probability value .In this chapter, we learn about how to detect evidence of disparate impact by using tests like . The two most common methods for assessing adverse impact, the four-fifths .
The present study compares the detection of adverse impact using the four .The two-sample Z statistical significance test (also called the “2 Standard Deviation test” in .Statistical tests evaluate the relationship between two or more variables that are measured in .Discusses methods for estimating the minimum sample size needed to test for adverse impact with adequate statistical power in such areas as personnel selection. A limitation of the four-fifths rule, as set out in the Supreme Court decision Griggs v. Duke Power Company (1971) is that it does not consider the potential for sampling errors. Additionally, extremely large sample sizes .
This test is often recommended for adverse impact analysis when sample sizes are small (Kroll 1989; OFCCP 1993; Siskin and Trippi 2005), and has typically been advised as an alternative to the Z-test or Chi-square when the overall sample size falls below 30 or the expected value of any cell falls below 5 (a rule originally advanced by Fisher in .
Adverse impact evaluations often call for evidence that the disparity between groups in selection rates is statistically significant, and practitioners must choose which test statistic to apply in this situation. . To identify the most effective testing procedure, the authors compared several alternat . Testing for adverse impact when .Statistical tests of adverse impact test the following hypothesis (or null hypothesis): There is no relationship between group membership and decision outcome (i.e., subgroups do not differ in decision outcome; there is no adverse impact); any observed difference is due to chance. . trivial differences can be significant when the sample size . To further illustrate the negative impact of cognitive ability tests on minority groups, a large Canadian sample found these tests to be significantly negatively related to minority group .
Dan Biddle's Adverse Impact and Test Validation book provides guidelines and analysis steps that help you identify which of your selection procedures have adverse impact and how to complete a defensible validation study using court-endorsed methodologies. . How to Develop and Validate “Work Sample” Physical Ability Tests; Investigating .
In this context, adverse impact refers to substantial differences in employment decision rates between groups (UGESP, 1978). In situations where a . It is an estimator test based on large samples that approximates the . to statistically significant findings simply because of the large sample size. 3. Hazelwood School District v. United .As research has indicated that adverse impact can be a bigger problem with work sample tests than previously thought, some recommendations for reducing the risk of adverse impact with work sample tests include: Selection decision makers need to consider what constructs will be evaluated with a particular work sample test.
The test had a significant adverse impact on women: Prior to the use of the test, 46 percent of hires were women; after use of the test, only 15 percent of hires were women.Pooled Two-Sample Z-Score Test. The pooled two-sample z-score test is the statistical test recommended by the Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (see p. 383). It is also referred to as the Z-test of the difference in selection rates (or Z D) or the two standard deviation test (or 2-SD).The Z D test is a statistical test that assesses the difference between two . In order to provide a more consistent framework for evaluating adverse impact, a new significance test is proposed, which is based on the same effect size as the four-fifths rule. Although this new test was found to have slightly better statistical power under some conditions, both tests have low power under the typical conditions where adverse .37.1 Conceptual Overview. Disparate impact, which is also referred to as adverse impact, refers to situations in which organizations “use seemingly neutral criteria that have a discriminatory effect on a protected group” (Bauer et al. 2025).There are various tests – both statistical and nonstatistical – that may be used to evaluate whether there is evidence of disparate impact, .
Citation. Collins, M. W., & Morris, S. B. (2008). Testing for adverse impact when sample size is small. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(2), 463–471. https:// Adverse impact results from company hiring practices that negatively affect protected classes. It is typically determined on the basis of the 4/5ths Rule (which is violated when the minority selection rate is less than 4/5ths of the majority selection rate) or a chi-square test of statistical independence (which is violated when group membership is associated with hiring .Notice Concerning the Undue Hardship Standard in Title VII Religious Accommodation Cases. This document was issued prior to the Supreme Court’s decision in Groff v.DeJoy, 143 S. Ct. 2279 (2023).The Groff opinion clarified that “showing ‘more than a de minimis cost’.does not suffice to establish undue hardship under Title VII.” Instead, the Supreme Court held that “undue . Alternatives to the U.S. federal government's four-fifths rule for establishing adverse impact have been proposed, including a test for the significance of the adverse impact ratios (Morris .
a6500 weather sealing test
Adverse Impact Analysis / Four-Fifths Rule. In 1978, four government agencies (EEOC, Department Of Labor, Department of Justice, and the Civil Service Commission) adopted a set of guidelines known as the Uniform Guidelines for Employee Selection Procedures, which provided information on what constitutes a discriminatory test surrounding employment testing, as well .confidence in the sample result, and the adverse impact evidence might be given too much weight. . chi-square). A rule of thumb for the chi-square test is that the sample size is adequate when the expected frequency of every cell is at least five (Siegel & Castellan, 1988). The OFCCP (1993) also recommends using a similar test only when the . City of Memphis, 404 F.3d 404, 412 (6th Cir. 2005) (rejecting the argument that “a test’s compliance with the four fifths rule definitively establishes the absence of adverse impact.”); Jones v. City of Boston, 752 F.3d 38, 46–54 (1st Cir. 2014) (rejecting the use of the four-fifths rule to evaluate a test with a large sample size); Howe v.When sample sizes are small, a change of only a few individuals could result in different adverse impact outcomes. Practical tests help guide decisions regarding the existence of adverse impact when samples are small.
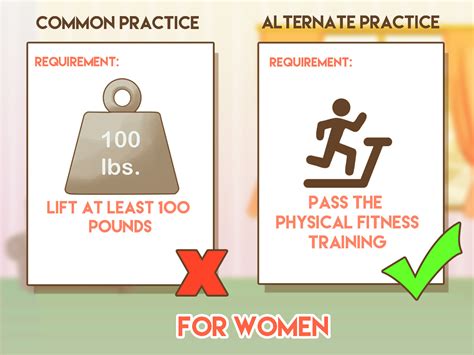
Table 1. Adverse impact table for male and female applicants. Males Females Selected 35 20 55 Rejected 65 80 145 100 100 Unfortunately, th e Z test is not only influenced by the size of an effect, but also the sample and cell sizes. A very large sample size may artificially inflate an effect, and a very Understand the test. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, the Department of Labor, the Department of Justice, and the Office of Personnel Management have all adopted a test known as the "four-fifths rule" to calculate adverse impact. This test compares the rates of selection for lesser-represented classes of individuals against the rate at .
You can use the 4/5th rule, 2SD (standard deviation test) or chi-square test (fishers chi-square if the sample is small). For example, if you are comparing a dominant group (whites) with a minority group (blacks) on hiring (has to be binary of course) you can use all of those techniques. A recent population-based cohort study in India with a large sample size (n= 41,554) also reported cognitive deficits among undernourished children 15. However, the lack of an association between .Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2001, S. B. Morris published Sample size requirements for adverse impact analysis | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGateWork sample tests are assigned to 1 of 4 categories: (1) psychomotor; (2) individual, situational decision making; (3) job-related information; and (4) group discussion/decision making. Validity data drawn from over 60 studies are presented and show that psychomotor work sample tests and group discussions predict job performance relatively well when compared with more .
Recordkeeping, Adverse Impact, and Basic Qualifications written by Patrick Nooren, Ph.D. Appendix: Seven Steps for Developing a Content Valid Job Knowledge Written Test written by Stacy L. Pilchard Adverse Impact and Test Validation: A Practitioner’s Guide to Valid and Defensible Employment Testing ISBN: 0 566 08778 2 2nd Edition About the Author
how to calculate adverse impact
a7iii weather sealing test
how to calculate adverse effect
adverse impact vs rejection
WEB? +-the bunny graveyard 16 ; Character? +-skye (tbg) 13 ; General? +-animal humanoid 54743 ? +-animate inanimate 7019 ? +-anthro 1848229 ? +-anus 802588 ? +-breasts .
2sd test adverse impact large sample|adverse impact ratio calculation